Multi-platform RabbitMQ Deployment
With ZeroMQ based VOLTTRON, multi-platform communication was accomplished in three different ways described below. Similar behavior can be accomplished with RabbitMQ-VOLTTRON as well.
Direct connection to remote instance - Write an agent that would connect to a remote instance directly.
Special agents - Use special agents such as forward historian/data puller agents that would forward/receive messages to/from remote instances. In RabbitMQ-VOLTTRON, we make use of the Shovel Plugin to achieve this behavior.
Multi-Platform RPC and PubSub - Configure VIP address of all remote instances that an instance has to connect to its $VOLTTRON_HOME/external_discovery.json and let the router module in each instance manage the connection and take care of the message routing for us. In RabbitMQ-VOLTTRON, we make use of the Federation Plugin to achieve this behavior.
Terminology
For all the three different ways of setting up multiplatform links, we first need to identify the upstream server and downstream server. The upstream server is the node that is publishing some message of interest; we shall refer to this node as the publisher node. The downstream server is the node that will receive messages from the upstream server; we shall refer to this node as the subscriber node. Note that upstream server & publisher node and downstream server & subscriber node will be used interchangeably for the rest of this guide.
Multi-Platform Communication With RabbitMQ SSL
RabbitMQ-VOLTTRON uses SSL based authentication for connection to the platform. This feature is extended to connection between multiple VOLTTRON platforms. The below figure shows the 2 remote VOLTTRON platforms can establish authentication connection to the other.
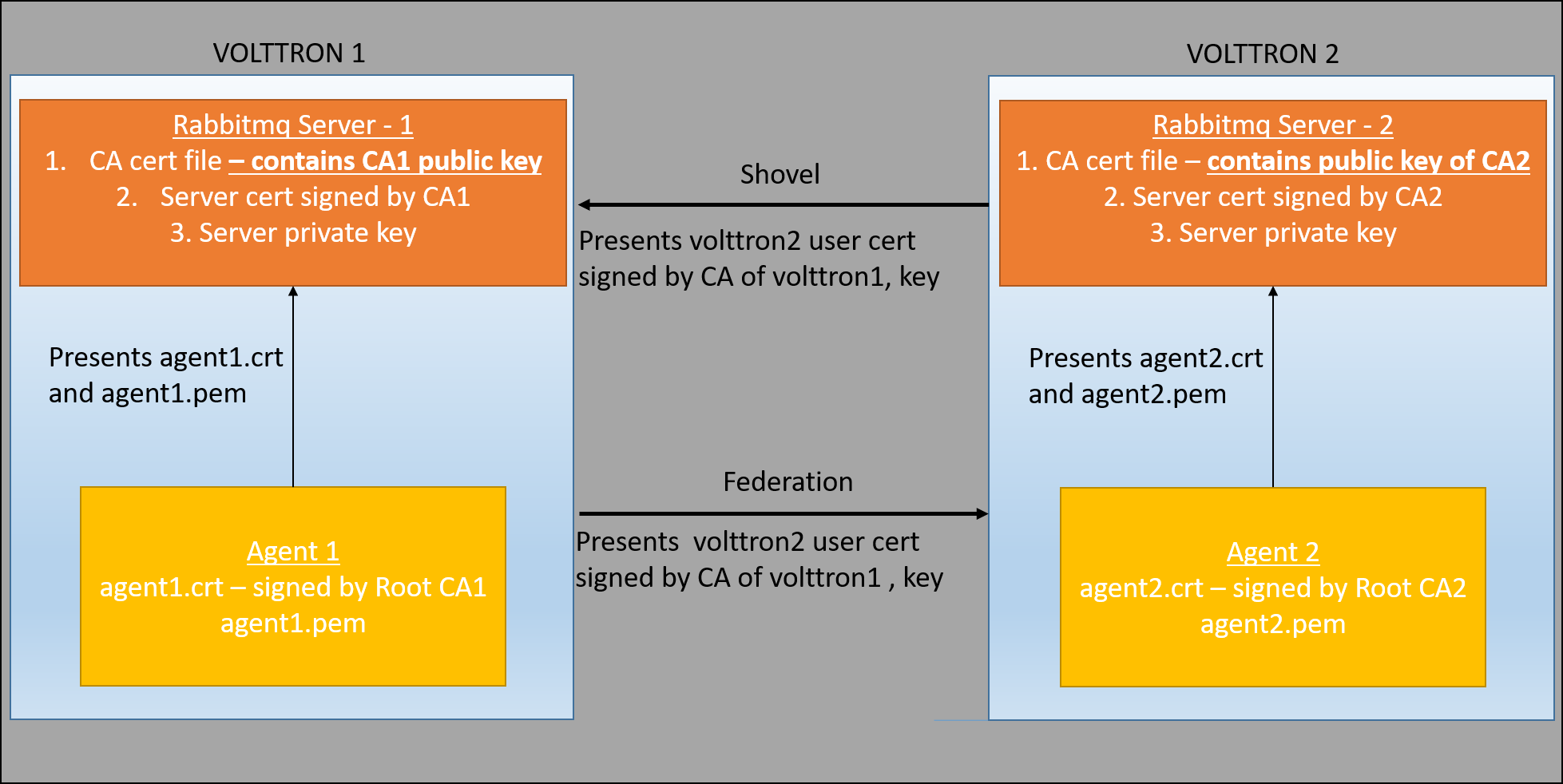
Suppose there are two virtual machines (VOLTTRON1 and VOLTTRON2) running single instances of RabbitMQ; VOLTTRON1 and VOLTTRON2 want to talk to each other via the federation or shovel plugins. For shovel/federation to have authenticated connection to the remote instance, it needs to have it’s public certificate signed by the remote instance’s CA. So as part of the shovel or federation creation steps, a certificate signing request is made to the remote instance. The admin of the remote instance should be ready to accept/reject such a request through VOLTTRON’s admin web interface. To facilitate this process, the VOLTTRON platform exposes a web-based server API for requesting, listing, approving, and denying certificate requests. For more detailed description, refer to Agent communication to Remote RabbitMQ instance. After the CSR request is accepted, an authenticated shovel/federation connection can be established.
Using the Federation Plugin
Note
Please make sure that a single instance of RabbitMQ VOLTTRON is setup before attempting to create a federation link platform installation steps for RMQ
Connecting multiple VOLTTRON instances can be done using the federation plugin. To create a RabbitMQ federation, we have to configure the downstream volttron instance to create federated exchange. A federated exchange links to other exchanges. In this case, the downstream federated exchange links to the upstream exchange. Conceptually, messages published to the upstream exchanges are copied to the federated exchange, as though they were published directly to the federated exchange.
Path: $VOLTTRON_HOME/rabbitmq_federation_config.yml
# Mandatory parameters for federation setup
federation-upstream:
volttron4: # hostname of upstream server
port: '5671'
virtual-host: volttron4
certificates:
csr: true
private_key: "path to private key" # For example, /home/volttron/vhome/test_fed/certificates/private/volttron1.federation.pem
public_cert: "path to public cert" # For example, /home/volttron/vhome/test_fed/certificates/federation/volttron2.volttron1.federation.crt
remote_ca: "path to CA cert" # For example, /home/volttron/vhome/test_fed/certificates/federation/volttron2_ca.crt
federation-user: volttron4.federation #<local instance name>.federation
volttron5: # hostname of upstream server
port: '5671'
virtual-host: volttron5
certificates:
csr: true
private_key: "path to private key"
public_cert: "path to public cert"
remote_ca: "path to CA cert"
federation-user: volttron5.federation #<local instance name>.federation
To setup federation on the VOLTTRON instance, run the following command on the downstream server:
vcfg rabbitmq federation [--config optional path to rabbitmq_federation_config.yml] [--max-retries optional maximum CSR retry attempt]
This establishes federation links to upstream servers. Here the default maximum retry attempt is set to 15. Once a federation link to the upstream server is established on the downstream server, the messages published on the upstream server become available to the downstream server as if it were published locally.
Multi-Platform RPC With Federation
For multi-platform RPC communication, federation links need to be established on both the VOLTTRON nodes. Once the federation links are established, RPC communication becomes fairly simple.
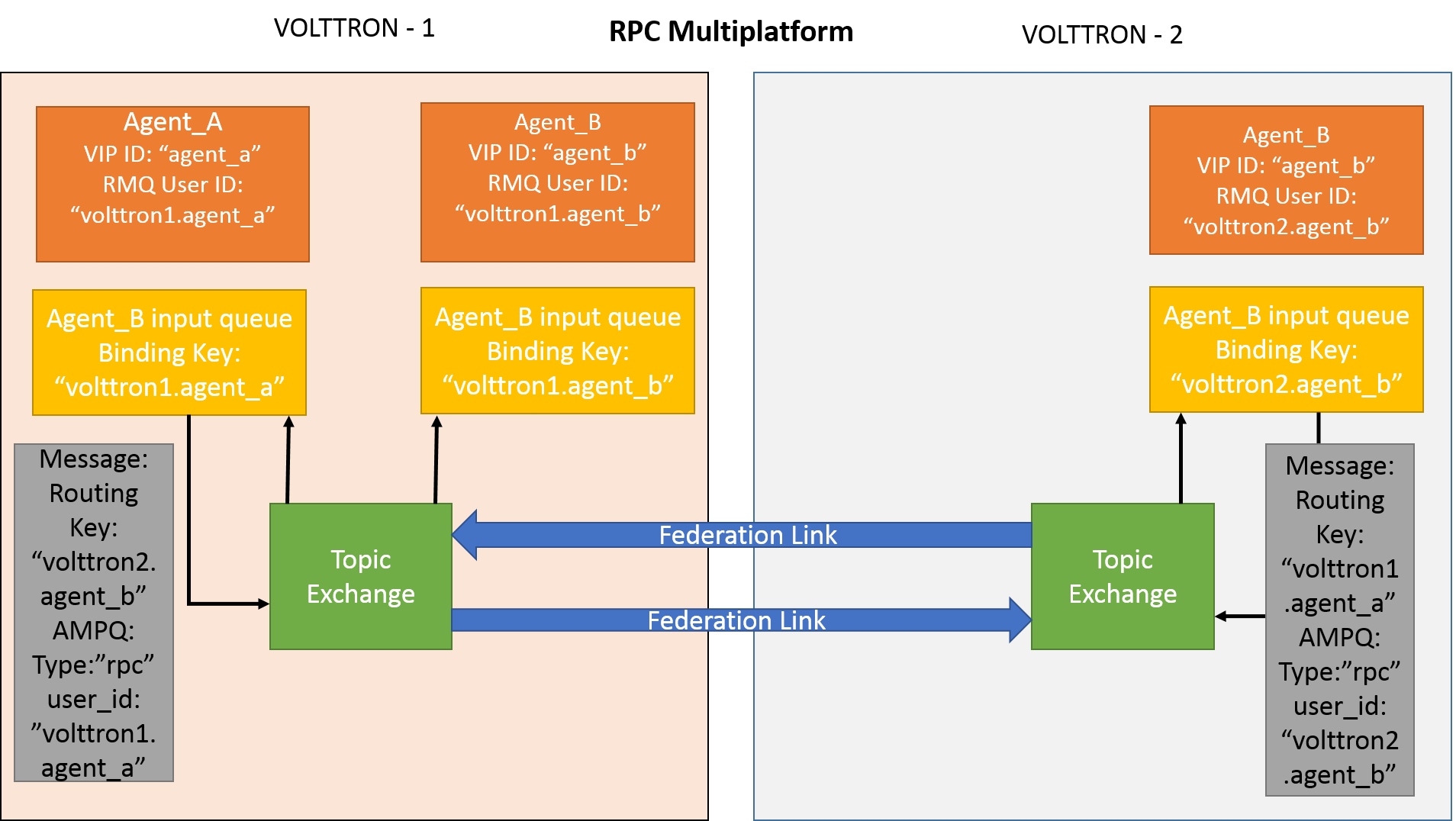
Consider Agent A on VOLTTRON instance “volttron1” on host “host_A” wants to make RPC call to Agent B on VOLTTRON instance “volttron2” on host “host_B”.
Agent A makes RPC call.
kwargs = {"external_platform": self.destination_instance_name}
agent_a.vip.rpc.call("agent_b", set_point, "point_name", 2.5, \**kwargs)
The message is transferred over federation link to VOLTTRON instance “volttron2” as both the exchanges are made federated.
The RPC subsystem of Agent B calls the actual RPC method and gets the result. It encapsulates the message result into a VIP message object and sends it back to Agent A on VOLTTRON instance “volttron1”.
The RPC subsystem on Agent A receives the message result and gives it to the Agent A application.
Multi-Platform PubSub With Federation
For multi-platform PubSub communication, it is sufficient to have a single federation link from the downstream server to the upstream server. In case of bi-directional data flow, two links have to established in both the directions.
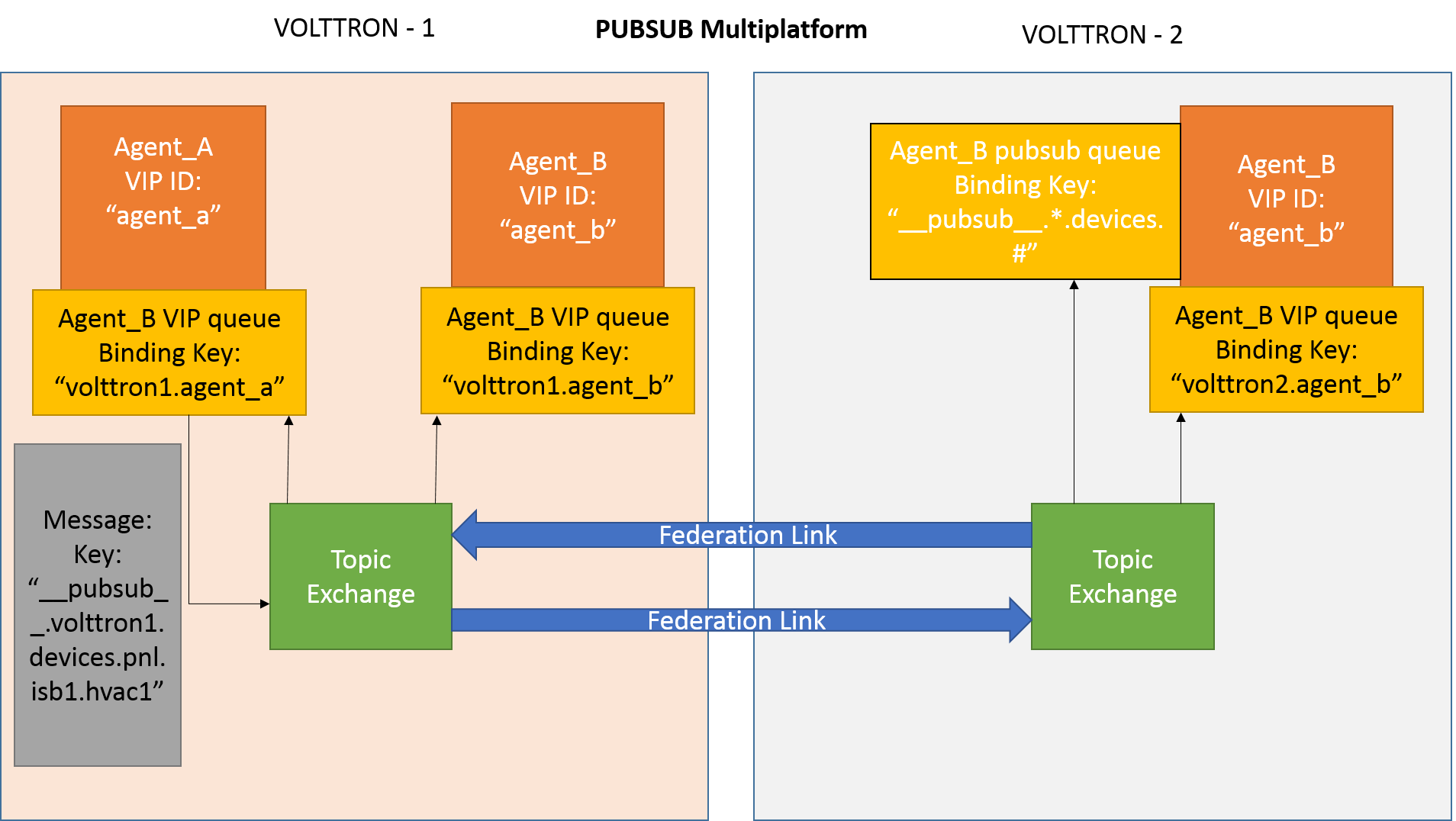
Consider Agent B on VOLTTRON instance “volttron2” on host “host_B” which wants to subscribe to messages from VOLTTRON instance “volttron2” on host “host_B”. First, a federation link needs to be established from “volttron2” to “volttron1”.
Agent B makes a subscribe call:
agent_b.vip.subscribe.call("pubsub", prefix="devices", all_platforms=True)
The PubSub subsystem converts the prefix to
__pubsub__.*.devices.#. Here,*indicates that agent is subscribing to thedevicestopic from all VOLTTRON platforms.A new queue is created and bound to VOLTTRON exchange with the above binding key. Since the VOLTTRON exchange is a federated exchange, any subscribed message on the upstream server becomes available on the federated exchange and Agent B will be able to receive it.
Agent A publishes message to topic devices/pnnl/isb1/hvac1
The PubSub subsystem publishes this message on its VOLTTRON exchange.
The message is received by the Pubsub subsystem of Agent A via the federation link.
Installation Steps
1. Setup two VOLTTRON instances using the instructions at platform installation steps for RMQ. Please note that each instance should have a unique instance name and should be running on a machine/VM that has a unique host name.
2. Identify upstream servers (publisher nodes) and downstream servers (collector nodes). To create a RabbitMQ federation, we have to configure upstream servers on the downstream server and make the VOLTTRON exchange “federated”.
On the downstream server (collector node)
vcfg rabbitmq federation [--config optional path to rabbitmq_federation_config.yml containing the details of the upstream hostname, port and vhost.] [--max-retries optional maximum CSR retry attempt]Example configuration for federation is available in examples/configurations/rabbitmq/rabbitmq_federation_config.yml
If no config file is provided, the script will prompt for hostname (or IP address), port, and vhost of each upstream node you would like to add and certificates for connecting to upstream server. For bi-directional data flow, we will have to run the same script on both the nodes.
If no config file is provided and certificates for connecting to upstream server have to be generated afresh, then the upstream server should be web enabled and admin should be ready to accept/reject incoming requests. Please refer to Multiple Platform Multiple Bus connection on how to enable web feature and accept/reject incoming authentication requests. Below image shows steps to follow to create a federation link from downstream instance “volttron1” to upstream instance “volttron2”.
On downstream server (collector node),
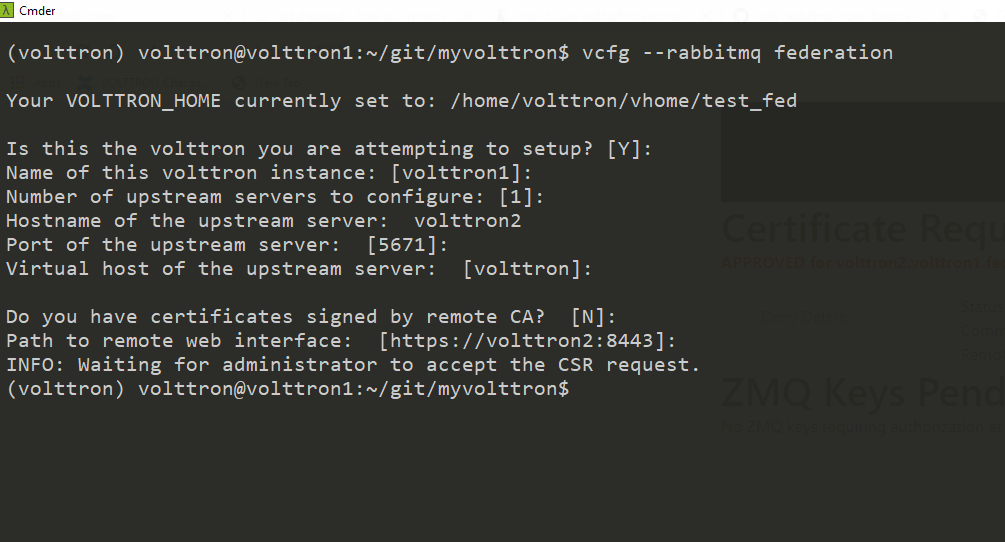
On upstream server (publisher node), Login to “https://volttron2:8443/index.html” in a web browser. You will see incoming CSR request from “volttron1” instance.
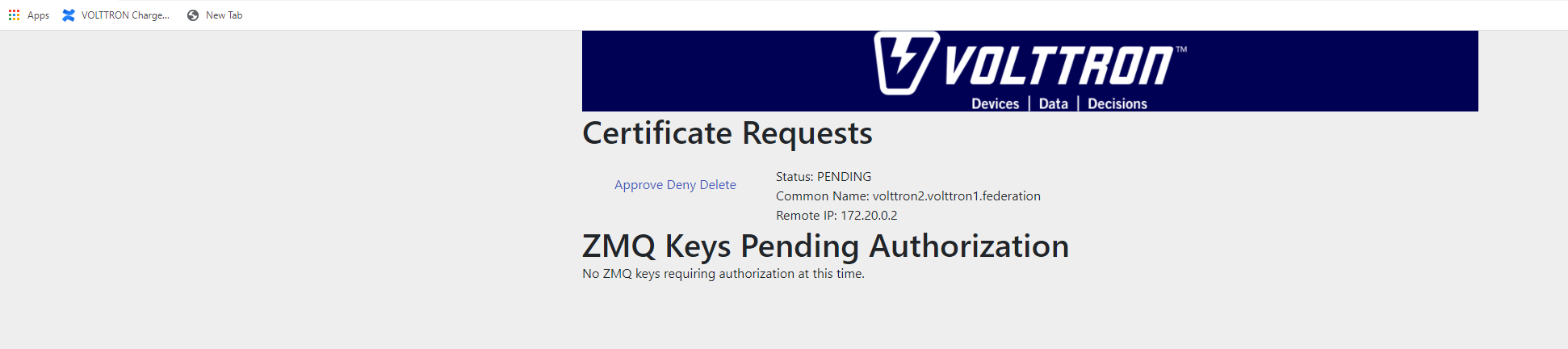
Accept the incoming CSR request from “volttron1” instance.
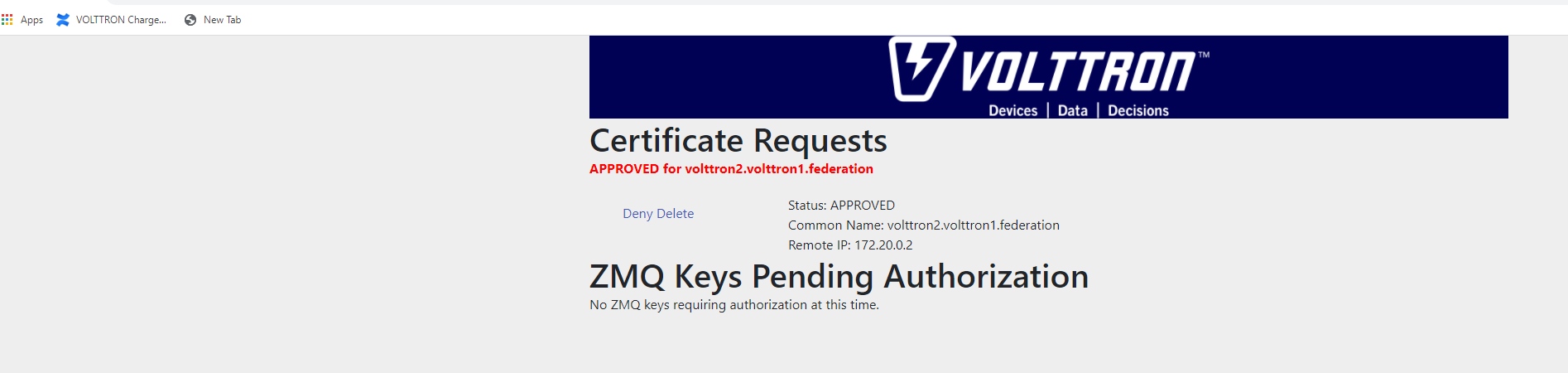
You can also find and accept the pending CSR via the command line, using the vctl auth remote sub-commands.
First list the pending certs and credentials.
vctl auth remote listUSER_ID ADDRESS STATUS volttron2.volttron1.federation 172.20.0.2 PENDINGApprove the pending CSR using the
approvecommand.vctl auth remote approve volttron2.volttron1.federationRun the
listcommand again to verify that the CSR has been approved.USER_ID ADDRESS STATUS volttron2.volttron1.federation 172.20.0.2 APPROVED
Test the federation setup.
On the downstream server run a listener agent which subscribes to messages from all platforms
vctl install examples/ListenerAgent --agent-config examples/ListenerAgent/config --startInstall platform driver, configure fake device on upstream server and start volttron and platform driver.
./stop-volttron vcfg --agent platform_driver ./start-volttron vctl start --tag platform_driverVerify that the listener agent in downstream VOLTTRON instance is able to receive the messages. The downstream volttron instance’s volttron.log should display device data scrapped by platform driver agent in upstream volttron instance.
Open ports and https service if needed. On Redhat based systems, ports used by RabbitMQ (defaults to 5671, 15671 for SSL, 5672 and 15672 otherwise) might not be open by default. Please contact system administrator to get ports opened on the downstream server.
Following are commands used on centos 7.
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=15671/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5671/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload
How to remove federation link
Using the management web interface
Log into management web interface using downstream server’s admin username. Navigate to admin tab and then to federation management page. The status of the upstream link will be displayed on the page. Click on the upstream link name and delete it.
Using “vctl” command on the upstream server.
vctl rabbitmq list-federation-links NAME STATUS upstream-volttron2-volttron running
Copy the upstream link name and run the below command to remove it.
vctl rabbitmq remove-federation-links upstream-volttron2-volttron Do you wish to delete certificates as well? [Y/n] y Removing certificate paths from VOLTTRON_HOME and from the config file
Note
These commands removes the federation parameter from RabbitMQ, deletes the certificates from VOLTTRON_HOME and certificate entries from rabbitmq_federation_config.yml on the publisher node. The remote admin must delete the remote certificates through admin web interface. If you need to rerun the federation command again for the same setup, then a fresh CSR request is made to the remote instance. The remote admin has to approve the new request as before.
Using the Shovel Plugin
Note
Please make sure that a single instance of RabbitMQ VOLTTRON is setup before attempting to create a shovel link platform installation steps for RMQ.
Shovels act as well-written client applications which move messages from a source to a destination broker. The below configuration shows how to setup a shovel to forward PubSub messages or perform multi-platform RPC communication from a local (i.e. publisher node) to a remote instance (i.e. subscriber node). The configuration expects hostname, port and virtual host values of the remote instance. It also needs certificates, namely private certs, public certificate signed by remote instance, and remote CA certificate.
Path: $VOLTTRON_HOME/rabbitmq_shovel_config.yml
# Mandatory parameters for shovel setup
shovel:
volttron2: # remote hostname
https-port: 8443
port: 5671
shovel-user: volttron1.shovelvolttron2 #<instance_name>.<unique name>
virtual-host: volttron
certificates:
private_cert: "path to private cert" # For example, /home/volttron/vhome/test_shovel/certificates/private/volttron1.shovelvolttron2.pem
public_cert: "path to public cert" # For example, /home/volttron/vhome/test_shovel/certificates/shovels/volttron2.volttron1.shovelvolttron2.crt
remote_ca: "path to CA cert" # For example, /home/volttron/vhome/test_shovel/certificates/shovels/volttron2_ca.crt
# Configuration to forward pubsub topics
pubsub:
# Identity of agent that is publishing the topic
platform.driver:
# Topic pattern to be forwarded
- devices
# Configuration to make remote RPC calls
rpc:
# Remote instance name
volttron2:
# List of pair of agent identities (local caller, remote callee)
- [scheduler, platform.actuator]
To forward PubSub messages, the topic and agent identity of the publisher agent is needed. To perform RPC, the instance name of the remote instance and agent identities of the local agent and remote agent are needed.
To configure the VOLTTRON instance to setup shovel, run the following command on the local instance.
vcfg rabbitmq shovel [--config optional path to rabbitmq_shovel_config.yml] [--max-retries optional maximum CSR retry attempt]
This sets up a shovel that forwards messages (either PubSub or RPC) from a local exchange to a remote exchange.
Multi-Platform PubSub With Shovel
After the shovel link is established for Pubsub, the below figure shows how the communication happens.
Note
For bi-directional pubsub communication, shovel links need to be created on both the nodes. The “blue” arrows show the shovel binding key. The pubsub topic configuration in $VOLTTRON_HOME/rabbitmq_shovel_config.yml gets internally converted to the shovel binding key: “__pubsub__.<local instance name>.<actual topic>”.
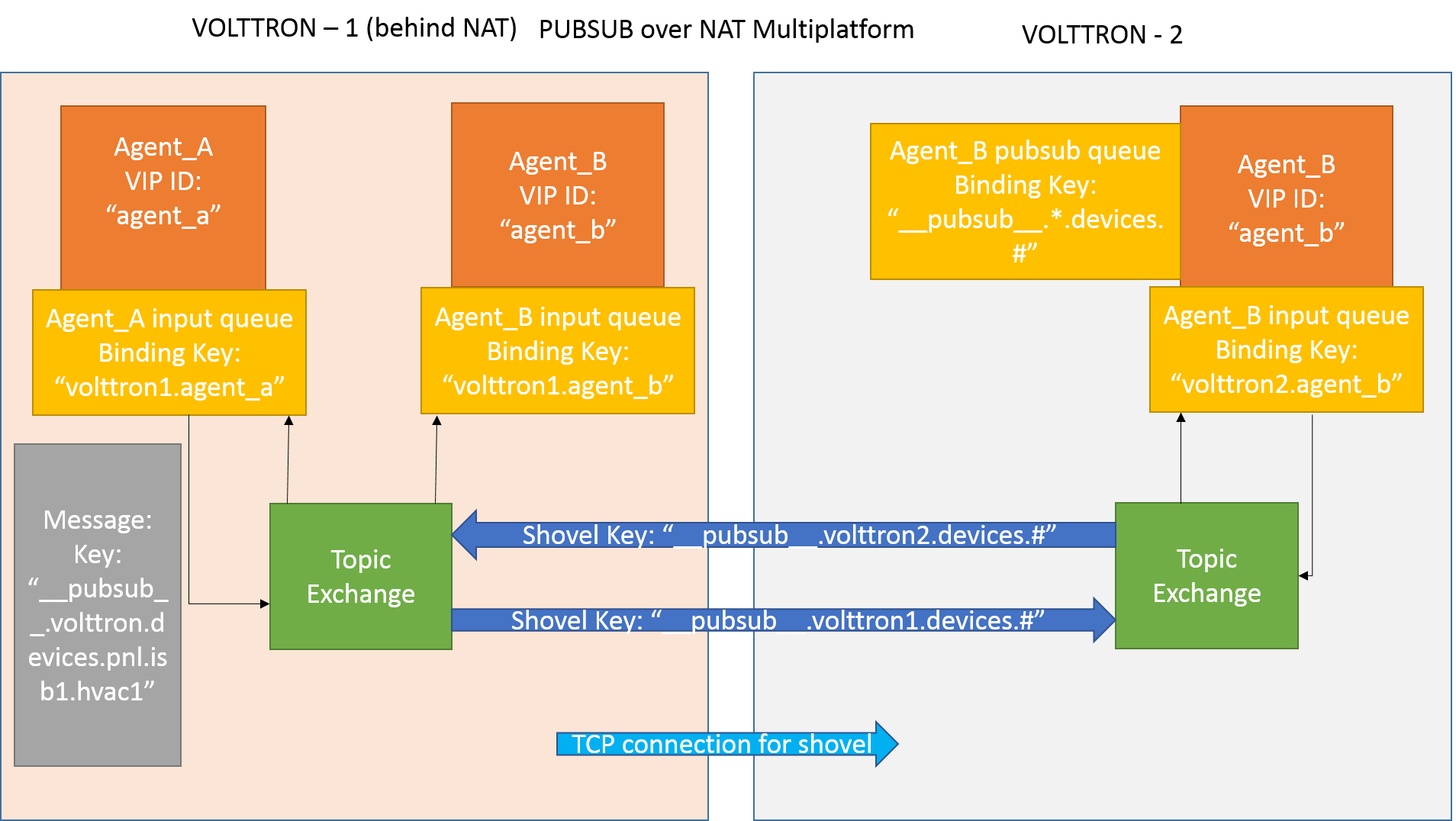
Now consider a case where shovels are setup in both the directions for forwarding “devices” topic.
Agent B makes a subscribe call to receive messages with topic “devices” from all connected platforms.
agent_b.vip.subscribe.call("pubsub", prefix="devices", all_platforms=True)
The PubSub subsystem converts the prefix to
__pubsub__.*.devices.#The*indicates that the agent is subscribing to the “devices” topic from all the VOLTTRON platforms.A new queue is created and bound to VOLTTRON exchange with above binding key.
Agent A publishes message to topic devices/pnnl/isb1/hvac1
PubSub subsystem publishes this message on its VOLTTRON exchange.
Because of the shovel link from VOLTTRON instance “volttron1” to “volttron2”, the message is forwarded from VOLTTRON exchange “volttron1” to “volttron2” and is picked up by Agent B on “volttron2”.
Multi-Platform RPC With Shovel
After the shovel link is established for multi-platform RPC, the below figure shows how the RPC communication happens.
Note
It is mandatory to have shovel links in both directions because RPC is a request-response type of communication. We will need to set the agent identities for caller and callee in the $VOLTTRON_HOME/rabbitmq_shovel_config.yml. The “blue” arrows show the resulting the shovel binding key.
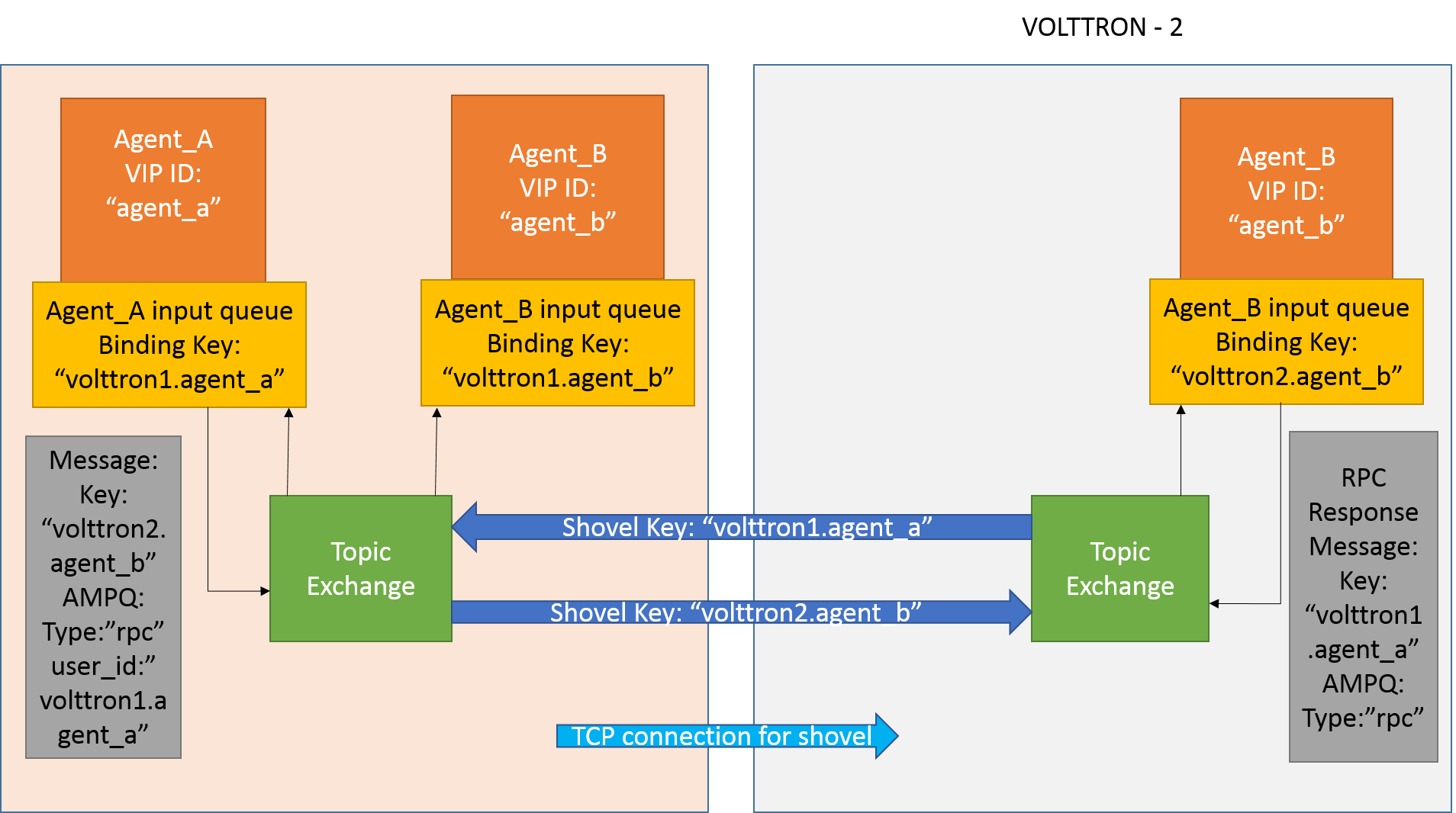
Consider Agent A on VOLTTRON instance “volttron1” on host “host_A” wants to make RPC call on Agent B on VOLTTRON instance “volttron2” on host “host_B”.
Agent A makes RPC call:
kwargs = {"external_platform": self.destination_instance_name}
agent_a.vip.rpc.call("agent_b", set_point, "point_name", 2.5, \**kwargs)
The message is transferred over shovel link to VOLTTRON instance “volttron2”.
The RPC subsystem of Agent B calls the actual RPC method and gets the result. It encapsulates the message result into a VIP message object and sends it back to Agent A on VOLTTRON instance “volttron1”.
The RPC subsystem on Agent A receives the message result and gives it to Agent A’s application.
Installation Steps for Pubsub Communication
For multi-platform communication over shovel, we need the connecting instances to trust each other. As part of the shovel
creation process, a certificate signing request is made to the remote instance. The admin of the remote instance has to
accept or reject such a request through VOLTTRON admin web interface. If accepted, a bundle containing a certificate
signed by the remote CA is sent as a response back to the local instance. Subsequently, shovel connection is
established with these certificates. If the user already has certificates signed by the remote CA, then that will be used for
connection. Otherwise, the user can run the command vcfg rabbitmq shovel and it will prompt the user to make a CSR request as part of shovel setup.
1. Setup two VOLTTRON instances using the steps described in installation section. Please note that each instance should have a unique instance name.
Identify the instance that is going to act as the “publisher” instance. Suppose “volttron1” instance is the “publisher” instance and “volttron2” instance is the “subscriber” instance. Then we need to create a shovel on “volttron1” to forward messages matching certain topics to remote instance “volttron2”.
On the publisher node,
vcfg rabbitmq shovel [--config optional path to rabbitmq_shovel_config.yml] [--max-retries optional maximum CSR retry attempt]
rabbitmq_shovel_config.yml should contain the details of the remote hostname, port, vhost, certificates for connecting to remote instance and list of topics to forward. Example configuration for shovel is available in examples/configurations/rabbitmq/rabbitmq_shovel_config.yml
For this example, let’s set the topic to “devices”
If no config file is provided, the script will prompt for hostname (or IP address), port, vhost, certificates for connecting to remote instance and list of topics for each remote instance you would like to add. For bi-directional data flow, we will have to run the same script on both the nodes.
b. If no config file is provided and certificates for connecting to remote instance have to be generated afresh, then the remote instance should be web enabled and admin should be ready to accept/reject incoming requests. Please refer to Multiple Platform Multiple Bus connection on how to enable web feature and accept/reject incoming authentication requests. Below image shows steps to follow to create a shovel to connect from “volttron1” to “volttron2” to publish “devices” topic from “volttron1” to “volttron2”.
On publisher node,
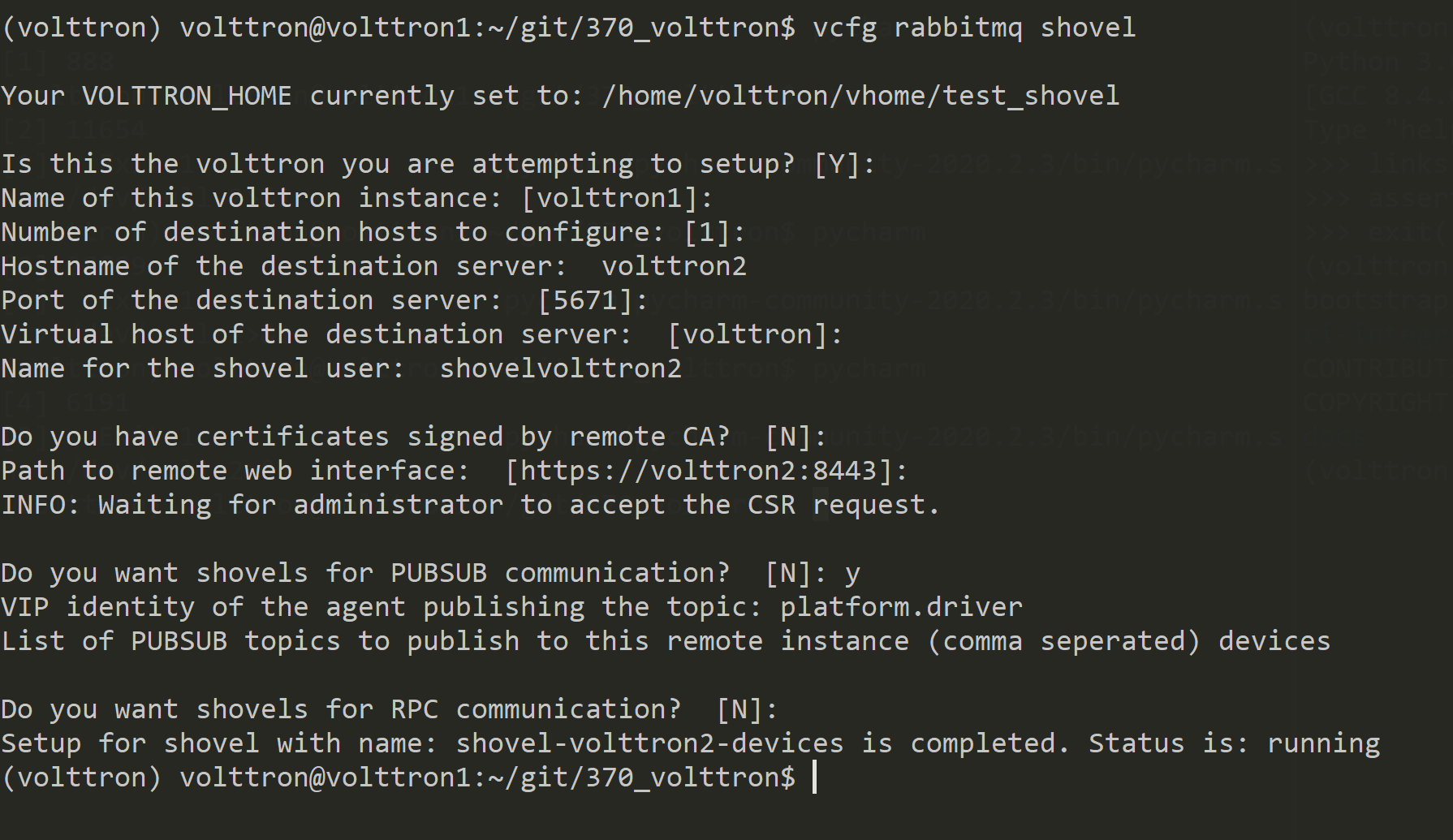
On subscriber node, login to “https://volttron2:8443/index.html” in a web browser. You will see an incoming CSR request from “volttron1” instance.
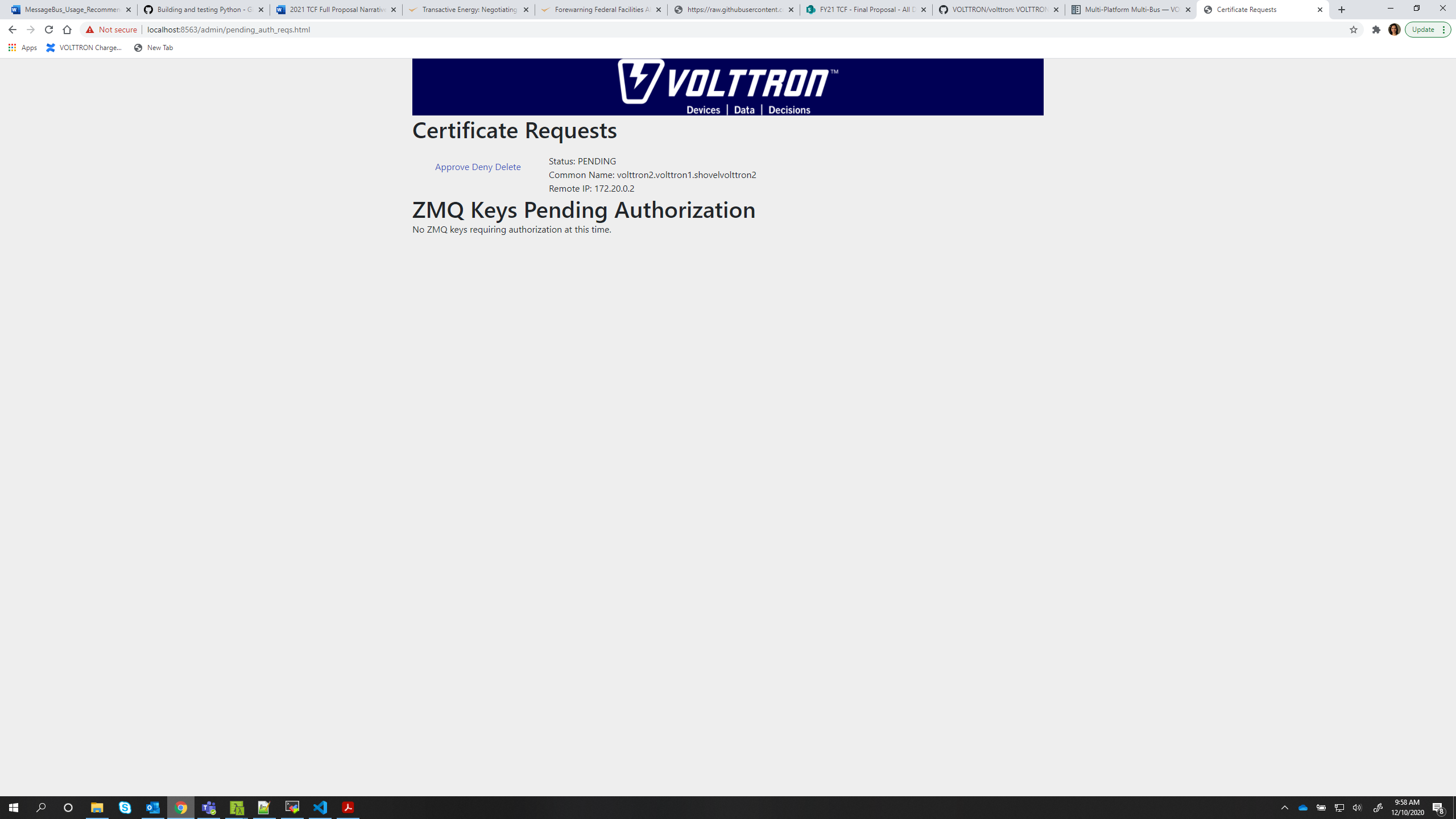
Accept the incoming CSR request from “volttron1” instance.
As before, you can find and accept the pending CSR via the command line, using the vctl auth remote sub-commands.
First list the pending certs and credentials.
vctl auth remote listUSER_ID ADDRESS STATUS volttron2.volttron1.shovelvolttron2 172.20.0.2 PENDING
Approve the pending CSR using the
approvecommand.vctl auth remote approve volttron2.volttron1.shovelvolttron2Run the
listcommand again to verify that the CSR has been approved.USER_ID ADDRESS STATUS volttron2.volttron1.shovelvolttron2 172.20.0.2 APPROVED
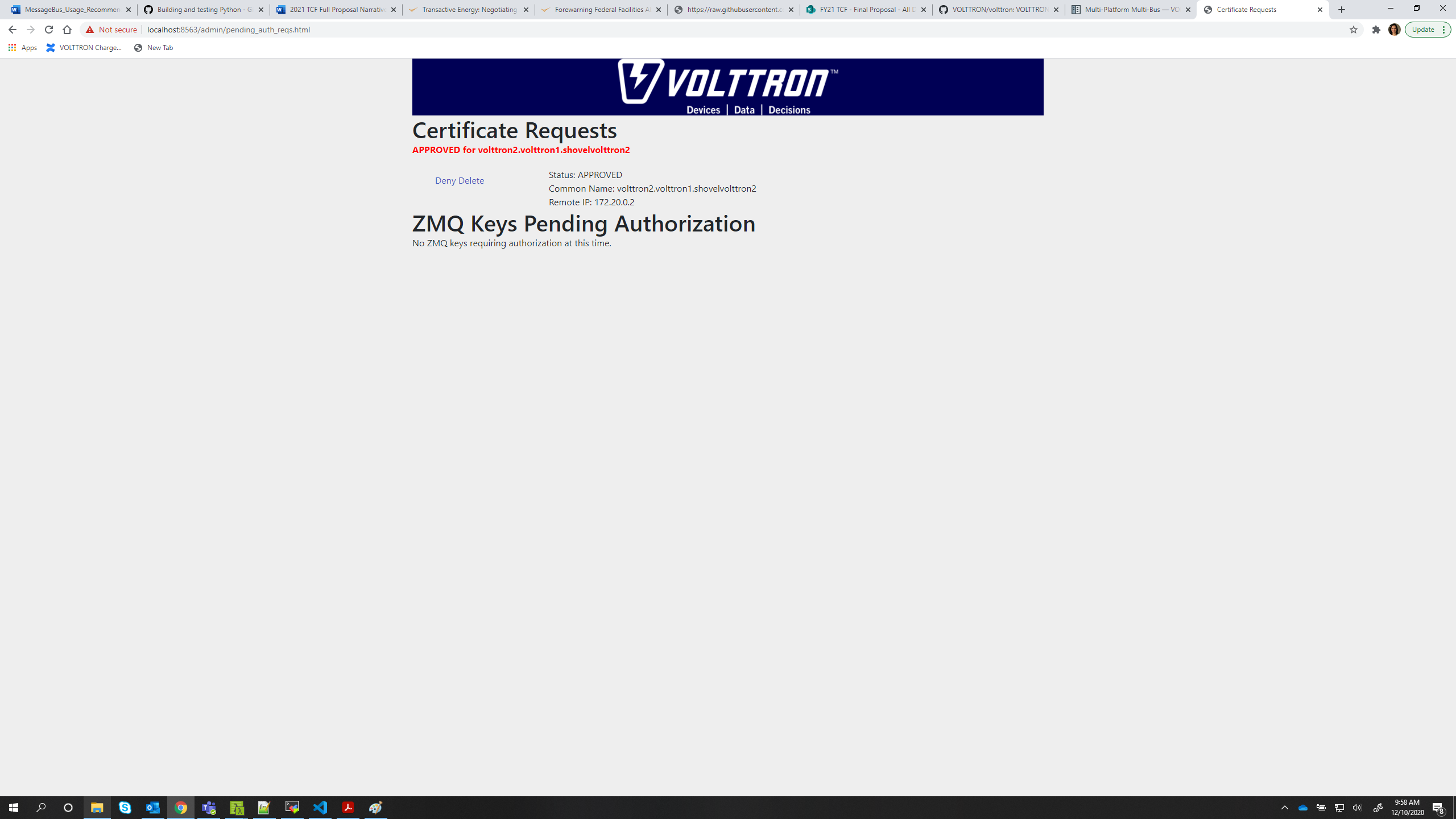
Test the shovel setup.
Start VOLTTRON on publisher and subscriber nodes.
On the publisher node, install and start a platform driver agent that publishes messages related to a fake device.
./stop-volttron vcfg --agent platform_driver ./start-volttron vctl start --tag platform_driver
On the subscriber node, run a listener agent which subscribes to messages from all platforms.
Open the file examples/ListenerAgent/listener/agent.py. Search for
@PubSub.subscribe('pubsub', '')and replace that line with@PubSub.subscribe('pubsub', 'devices', all_platforms=True)Install the listener
vctl install examples/ListenerAgent --agent-config examples/ListenerAgent/config --start
Verify listener agent in downstream VOLTTRON instance can receive the messages. The downstream volttron instance’s volttron.log should display device data scrapped by the platform driver agent in the upstream volttron instance.
How to remove the shovel setup.
On the subscriber node, remove the shovel on using the management web interface
Log into management web interface using publisher instance’s admin username. Navigate to admin tab and then to shovel management page. The status of the shovel will be displayed on the page. Click on the shovel name and delete the shovel.
On the publisher node, run the following “vctl” commands:
vctl rabbitmq list-shovel-links NAME STATUS SRC_URI DEST_URI SRC_EXCHANGE_KEY shovel-volttron2-devices running amqps://volttron1:5671/volttron amqps://volttron2:5671/volttron __pubsub__.volttron1.devices.#
Copy the shovel name and run following command to remove it.
vctl rabbitmq remove-shovel-links shovel-volttron2-devices Do you wish to delete certificates as well? [Y/n] y Removing certificate paths from VOLTTRON_HOME and from the config file
Note
These commands removes the shovel parameter from RabbitMQ, deletes the certificates from VOLTTRON_HOME and certificate entries from rabbitmq_shovel_config.yml on the publisher node. The remote admin must delete the remote certificates through admin web interface. If you need to rerun the federation command again for the same setup, then a fresh CSR request is made to the remote instance. The remote admin has to approve the new request as before.