Aggregate Historian
Description
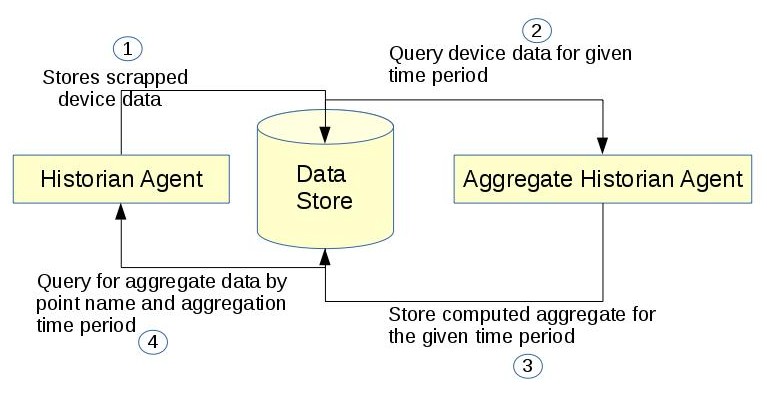
An aggregate historian computes aggregates of data stored in a given volttron historian’s data store. It runs periodically to compute aggregate data and store it in new tables/collections in the historian’s data store. Each regular historian ( BaseHistorian ) needs a corresponding aggregate historian to compute and store aggregates of the data collected by the regular historian.
Software Interfaces
Data Collection - Data store that the aggregate historian uses as input source needs to be up. Access to it should be provided using an account that has create, read, and write privileges. For example, a MongoAggregateHistorian needs to be able to connect to the mongodb used by MongoHistorian using an account that has read and write access to the db used by the MongoHistorian.
Data retrieval Aggregate Historian Agent does not provide api for retrieving the aggregate data collected. Use Historian agent’s query interface. Historian’s query api will be modified as below
topic_name can now be a list of topic names or a single topic
Two near optional parameters have been added to the query api - agg_type (aggregation type), agg_period (aggregation time period). Both these parameters are mandatory for query aggregate data.
New api to get the list of aggregate topics available for querying
User Interfaces
Aggregation agent requires user to configure the following details as part of the agent configuration file
Connection details for historian’s data store (same as historian agent configuration)
- List of aggregation groups where each group contains:
Aggregation period - integer followed by m/h/d/w/M (minutes, hours, days, weeks or months)
Boolean parameter to indicate if aggregation periods should align to calendar times
Optional collection start time in utc. If not provided, aggregation collection will start from current time
List of aggregation points with topic name, type of aggregation (sum, avg, etc.), and minimum number of records that should be available for the aggregate to be computed
Topic name can be specified either as a list of specific topic names (topic_names=[topic1, topic2]) or a regular expression pattern (topic_name_pattern=”Building1/device_*/Zone*temperature”)
When aggregation is done for a single topic then name of topic will be used for the computed aggregation as well. You could optionally provide a unique aggregation_topic_name
When topic_name_pattern or multiple topics are specified a unique aggregate topic name should be specified for the collected aggregate. Users can query for the collected aggregate data using this aggregate topic name.
User should be able to configure multiple aggregations done with the same time period/time interval and these should be time synchronized.
Functional Capabilities
Should run periodically to compute aggregate data.
Same instance of the agent should be able to collect data at more than one time interval
For each configured time period/interval agent should be able to collect different type of aggregation for different topics/points
Support aggregation over multiple topics/points
Agent should be able to handle and normalize different time units such as minutes, hours, days, weeks and months
Agent should be able to compute aggregate both based on wall clock based time intervals and calendar based time interval. For example, agent should be able to calculate daily average based on 12.00AM to 11.59PM of a calendar day or between current time and the same time the previous day.
Data should be stored in such a way that users can easily retrieve multiple aggregate topics data within a given time interval
Data Structure
Collected aggregate data should be stored in the historian data store into new collection or tables and should be accessible by historian agent’s query interface. Users should easily be able to query aggregate data of multiple points for which data is time synchronized.
Use Cases
Collect monthly average of multiple topic using data from MongoDBHistorian
1. Create a configuration file with connection details from Mongo Historian configuration file and add additional aggregation specific configuration
{
# configuration from mongo historian - START
"connection": {
"type": "mongodb",
"params": {
"host": "localhost",
"port": 27017,
"database": "mongo_test",
"user": "test",
"passwd": "test"
}
},
# configuration from mongo historian - START
"aggregations":[
# list of aggregation groups each with unique aggregation_period and
# list of points that needs to be collected
{
"aggregation_period": "1M",
"use_calendar_time_periods": true,
"utc_collection_start_time":"2016-03-01T01:15:01.000000",
"points": [
{
"topic_names": ["Building/device/point1", "Building/device/point2"],
"aggregation_topic_name":"building/device/point1_2/month_sum",
"aggregation_type": "avg",
"min_count": 2
}
]
}
]
}
In the above example configuration, here is what each field under “aggregations” represent
aggregation_period: can be minutes(m), hours(h), weeks(w), or months(M)
- use_calendar_time_periods: true or false - Should aggregation period align to calendar time periods. Default False. Example,
if “aggregation_period”:”1h” and “use_calendar_time_periods”: false, example periods: 10.15-11.15, 11.15-12.15, 12.15-13.15 etc.
if “aggregation_period”:”1h” and “use_calendar_time_periods”: true, example periods: 10.00-11.00, 11.00-12.00, 12.00-13.00 etc.
if “aggregation_period”:”1M” and “use_calendar_time_periods”: true, aggregation would be computed from the first day of the month to last day of the month
if “aggregation_period”:”1M” and “use_calendar_time_periods”: false, aggregation would be computed with a 30 day interval based on aggregation collection start time
utc_collection_start_time: The time from which aggregation computation should start. If not provided this would default to current time.
- points: List of points, its aggregation type and min_count
topic_names: List of topic_names across which aggregation should be computed. aggregation_topic_name: Unique name given for this aggregate. Optional if aggregation is for a single topic. aggregation_type: Type of aggregation to be done. Please see Constraints and Limitations
min_count: Optional. Minimum number of records that should exist within the configured time period for a aggregation to be computed.
install and starts the aggregate historian using the above configuration
3. Query aggregate data: Query using historian’s query api by passing two additional parameters - agg_type and agg_period
result1 = query_agent.vip.rpc.call('platform.historian',
'query',
topic='building/device/point1_2/month_sum',
agg_type='avg',
agg_period='1M',
count=20,
order="FIRST_TO_LAST").get(10)
Collect weekly average(sunday to saturday) of single topic using data from MongoDBHistorian
- Create a configuration file with connection details from Mongo Historian configuration file and add additional aggregation specific configuration. The configuration file should be similar to the first use case except
aggregation_period: “1w”,
topic_names: [“Building/device/point1”], #topic for which you want to compute aggregation
aggregation_topic_name need not be provided
install and starts the aggregate historian using the above configuration
3. Query aggregate data: Query using historian’s query api by passing two additional parameters - agg_type and agg_period. topic_name will be the same as the point name for which aggregation is collected
result1 = query_agent.vip.rpc.call('platform.historian',
'query',
topic='Building/device/point1',
agg_type='avg',
agg_period='1w',
count=20,
order="FIRST_TO_LAST").get(10)
Collect hourly average for multiple topics based on topic_name pattern
- Create a configuration file with connection details from Mongo Historian configuration file and add additional aggregation specific configuration. The configuration file should be similar to the first use case except
aggregation_period: “1h”,
Insetead of topic_names provide topic_name_pattern. For example, “topic_name_pattern”:”Building1/device_a*/point1”
aggregation_topic_name provide a unique aggregation topic name
install and starts the aggregate historian using the above configuration
3. Query aggregate data: Query using historian’s query api by passing two additional parameters - agg_type and agg_period. topic_name will be the same as the point name for which aggregation is collected
result1 = query_agent.vip.rpc.call('platform.historian',
'query',
topic="unique aggregation_topic_name provided in configuration",
agg_type='avg',
agg_period='1h',
count=20,
order="FIRST_TO_LAST").get(10)
Collect 7 day average of two topics and time synchronize them for easy comparison
1. Create a configuration file with connection details from Mongo Historian configuration file and add additional aggregation specific configuration. The configuration file should be similar to the below example
{
# configuration from mongo historian - START
"connection": {
"type": "mongodb",
"params": {
"host": "localhost",
"port": 27017,
"database": "mongo_test",
"user": "test",
"passwd": "test"
}
},
# configuration from mongo historian - START
"aggregations":[
# list of aggregation groups each with unique aggregation_period and
# list of points that needs to be collected
{
"aggregation_period": "1w",
"use_calendar_time_periods": false, #compute for last 7 days, then the next and so on..
"points": [
{
"topic_names": ["Building/device/point1"],
"aggregation_type": "avg",
"min_count": 2
},
{
"topic_names": ["Building/device/point2"],
"aggregation_type": "avg",
"min_count": 2
}
]
}
]
}
install and starts the aggregate historian using the above configuration
3. Query aggregate data: Query using historian’s query api by passing two additional parameters - agg_type and agg_period. provide the list of topic names for which aggregate was configured above. Since both the points were configured within a single “aggregations” array element, their aggregations will be time synchronized
result1 = query_agent.vip.rpc.call('platform.historian',
'query',
topic=['Building/device/point1''Building/device/point2'],
agg_type='avg',
agg_period='1w',
count=20,
order="FIRST_TO_LAST").get(10)
Results will be of the format
{'values': [
['Building/device/point1', '2016-09-06T23:31:27.679910+00:00', 2],
['Building/device/point1', '2016-09-15T23:31:27.679910+00:00', 3],
['Building/device/point2', '2016-09-06T23:31:27.679910+00:00', 2],
['Building/device/point2', '2016-09-15T23:31:27.679910+00:00', 3]],
'metadata': {}}
Qurey list of aggregate data collected
result = query_agent.vip.rpc.call('platform.historian',
'get_aggregate_topics').get(10)
The result will be of the format:
[(aggregate topic name, aggregation type, aggregation time period, configured list of topics or topic name pattern), ...]
This shows the list of aggregation currently being computed periodically
Qurey list of supported aggregation types
result = query_agent.vip.rpc.call(
AGG_AGENT_VIP,
'get_supported_aggregations').get(timeout=10)
Constraints and Limitations
Initial implementation of this agent will not support any data filtering for raw data before computing data aggregation
Initial implementation should support all aggregation types directly supported by underlying data store. End user input is needed to figure out what additional aggregation methods are to be supported
MySQL
Name
Description
AVG()
Return the average value of the argument
BIT_AND()
Return bitwise AND
BIT_OR()
Return bitwise OR
BIT_XOR()
Return bitwise XOR
COUNT()
Return a count of the number of rows returned
GROUP_CONCAT()
Return a concatenated string
MAX()
Return the maximum value
MIN()
Return the minimum value
STD()
Return the population standard deviation
STDDEV()
Return the population standard deviation
STDDEV_POP()
Return the population standard deviation
STDDEV_SAMP()
Return the sample standard deviation
SUM()
Return the sum
VAR_POP()
Return the population standard variance
VAR_SAMP()
Return the sample variance
VARIANCE()
Return the population standard variance
SQLite
Name
Description
AVG()
Return the average value of the argument
COUNT()
Return a count of the number of rows returned
GROUP_CONCAT()
Return a concatenated string
MAX()
Return the maximum value
MIN()
Return the minimum value
SUM()
Return sum of all non-NULL values in the group. If there are no non-NULL input rows then returns NULL .
TOTAL()
Return sum of all non-NULL values in the group.If there are no non-NULL input rows returns 0.0
MongoDB
Name
Description
SUM
Returns a sum of numerical values. Ignores non-numeric values
AVG
Returns a average of numerical values. Ignores non-numeric values
MAX
Returns the highest expression value for each group.
MIN
Returns the lowest expression value for each group.
FIRST
Returns a value from the first document for each group. Order is only defined if the documents are in a defined order.
LAST
Returns a value from the last document for each group. Order is only defined if the documents are in a defined order.
PUSH
Returns an array of expression values for each group
ADDTOSET
Returns an array of unique expression values for each group. Order of the array elements is undefined.
STDDEVPOP
Returns the population standard deviation of the input values
STDDEVSAMP
Returns the sample standard deviation of the input values